Lifestyle and Men’s Health
Nutrition and Its Effects on Men’s HealthProper nutrition is a cornerstone of male sexual health. Foods rich in antioxidants improve blood circulation, supporting erectile function. Omega-3 fatty acids increase testosterone production, while minerals like zinc and selenium enhance sperm quality.
Key Nutrients:Zinc: Vital for testosterone production and sperm health
L-Arginine: Improves blood flow by boosting nitric oxide production
Vitamin D: Essential for hormonal balance and bone health
Folate: Important for protecting sperm DNA
Vitamins C and E: Provide antioxidant protection
Foods to AvoidProcessed foods, high-sugar products, and excessive saturated fats negatively affect men’s health. These contribute to obesity, reduce testosterone levels, and impair cardiovascular health. High sodium intake can raise blood pressure and harm sexual function.
Harmful Dietary Habits:Excessive sugar intake: Causes insulin resistance and hormonal imbalance
Trans fats: Damage vascular health and increase inflammation
Excessive alcohol: Suppresses testosterone production and impairs liver function
High sodium: Raises blood pressure, affecting sexual performance
Physical Activity and Exercise
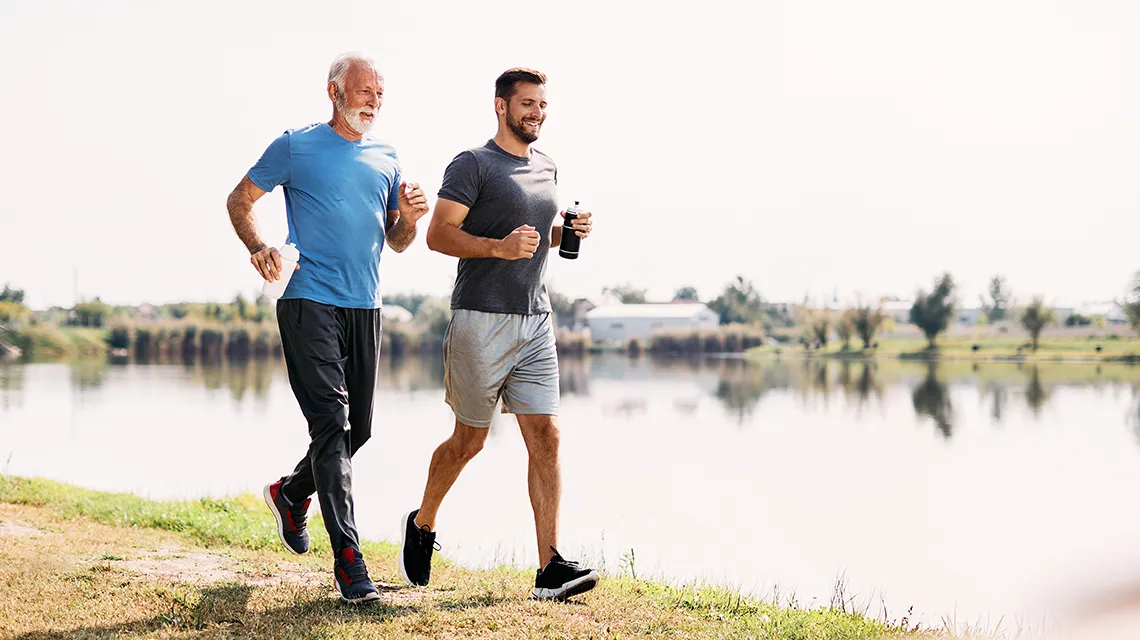
Benefits of Cardiovascular ExerciseRegular aerobic exercise improves heart health and supports sexual function. Activities like running, swimming, cycling, and walking increase blood flow and reduce erectile dysfunction risk. At least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise weekly is recommended for men’s health.
Effects of Cardiovascular Exercise on Sexual Health:Improved blood flow
Strengthened endothelial function
Reduced stress hormones
Increased energy levels
Improved body composition
Strength Training and Hormonal EffectsWeight training is one of the most effective natural methods to increase testosterone production. Compound movements engaging large muscle groups—such as squats, deadlifts, and bench presses—optimize hormonal response and play a critical role in balancing male hormones.
Benefits of Strength Training:Increased testosterone levels
Preservation and growth of muscle mass
Improved bone density
Accelerated metabolism
Boosted self-confidence
Kegel Exercises and Pelvic Floor HealthStrengthening pelvic floor muscles significantly enhances sexual performance. Kegel exercises improve erection quality, help control premature ejaculation, and support prostate health. Regular practice yields noticeable results.
Stress Management and Mental Health
Effects of Stress on Men’s HealthChronic stress raises cortisol levels, suppressing testosterone production. This results in decreased libido, erectile dysfunction, and reduced energy. Stress also adversely affects the cardiovascular system, indirectly impairing sexual health.
Negative Effects of Stress:Hormonal imbalance
Weakened immune system
Reduced sleep quality
Lowered libido
Decline in overall quality of life
Mental Health and Sexual PerformanceDepression and anxiety profoundly affect sexual function through psychological and physiological mechanisms. Professional psychological support and therapeutic interventions are critical to restoring sexual health.
Sleep Quality and Hormonal Balance
Impact of Sleep on Testosterone ProductionQuality sleep is vital for optimal testosterone synthesis, which mainly occurs during deep sleep phases. Sleep deprivation dramatically lowers hormone levels, negatively affecting sexual function.
Sleep and Hormonal Health:7–9 hours of quality nighttime sleep
Regular sleep-wake cycles
Optimized sleep environment
Avoidance of electronic devices before bed
Limiting caffeine and alcohol intake
Effects of Sleep Disorders on Sexual HealthSleep disorders such as sleep apnea reduce oxygen levels, impairing overall health. These disorders affect the cardiovascular system and sexual function. Early diagnosis and treatment of sleep disorders are crucial for men’s health.
Harmful Habits and Their Effects
Smoking and Sexual HealthSmoking damages blood vessels, severely impacting sexual function. Nicotine’s vasoconstrictive effect reduces penile blood flow, causing erectile dysfunction. Benefits of quitting smoking often begin within weeks.
Harmful Effects of Smoking:Vascular damage and reduced blood flow
Decline in sperm quality
Hormonal imbalance
Increased oxidative stress
Shortened overall lifespan
Alcohol Consumption and LimitsWhile moderate alcohol intake may have some health benefits, excessive consumption seriously threatens male health. Alcohol suppresses testosterone production, impairs liver function, and damages the nervous system.
Safe Alcohol Consumption:Maximum two standard drinks daily
At least two alcohol-free days weekly
Preference for quality alcoholic beverages
Seek professional help if consumption is excessive
Drug UseRecreational drug use can cause permanent damage to the male reproductive system. Cannabis, cocaine, and other substances reduce sperm quality, disrupt hormonal balance, and impair sexual function.
Environmental Factors and Toxin Exposure
Endocrine Disruptors and Men’s HealthPlasticizers, pesticides, and chemicals encountered in modern life can disrupt the endocrine system, creating estrogen-like effects that disturb male hormonal balance. Avoiding BPA, phthalates, and other chemicals is important for protecting men’s health.
Protection Against Environmental Toxins:Limit use of plastic food containers
Prefer organic foods
Use natural cleaning products
Pay attention to air quality
Use water filters
Electromagnetic RadiationRadiation emitted by devices such as cell phones and laptops can negatively affect sperm quality. Keeping devices away from the body and limiting usage duration is recommended to preserve reproductive health.
Age Factor and Men’s Health
Andropause and Hormonal ChangesAge-related hormonal changes in men, known as andropause, include decreased testosterone levels, muscle loss, reduced energy, and sexual dysfunction. Early intervention and lifestyle changes can slow this process.
Prostate Health and LifestyleProstate health is an important consideration as men age. Healthy lifestyle habits, including regular exercise, balanced nutrition, and stress management, support prostate well-being.
Maintaining Sexual Health in Older AgeActive and satisfying sexual life is possible in later years. Lifestyle modifications, regular health check-ups, and medical interventions when needed help preserve sexual health.
Sexual Activity Without a Partner and Health
Masturbation and Health EffectsMasturbation is a normal and healthy sexual behavior. When done moderately, it supports prostate health and reduces stress. However, excessive masturbation may lead to psychological problems and performance anxiety.
Pornography Use and EffectsExcessive pornography consumption can create unrealistic expectations and contribute to performance anxiety. This addictive behavior may reduce satisfaction in real relationships. Conscious use and professional support when needed are important.
Preventive Health Approach
Regular Check-up Areas:Cardiovascular system evaluation
Hormonal profile analysis
Prostate health monitoring
Diabetes and metabolic syndrome screening
Sexual function assessment
Laboratory TestsBlood tests are essential tools for objective assessment of men’s health. Testosterone levels, lipid profile, blood sugar, and vitamin levels should be regularly monitored. These tests also help evaluate the impact of lifestyle changes.
Specialist Follow-upRegular care by urology, endocrinology, and cardiology specialists is necessary for professional management of men’s health. Multidisciplinary approaches are recommended especially for men with risk factors.
Social Factors and Relationships
Importance of Partner RelationshipsHealthy partner relationships are vital components of men’s health. Supportive relationships reduce stress levels and improve overall quality of life. Communication skills and conflict resolution directly affect relationship quality.
Social Support SystemsStrong social connections support mental health and enhance coping with stress. Friendships, family bonds, and community involvement play important roles in maintaining men’s health.
Work-Life BalanceEstablishing a work-life balance is critical for men’s health. Excessive work, insufficient rest, and social isolation negatively impact health. Adopting a balanced lifestyle is necessary for long-term well-being.
Digital DetoxExcessive technology use disrupts sleep quality and leads to social isolation. Digital detox practices help protect mental health and enhance real-life experiences.